
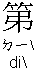
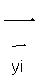


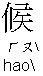
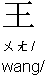
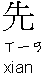
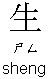 :
: 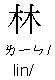
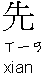
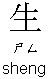
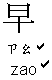 ,
, 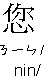
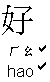
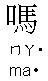 ?
? 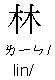
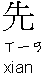
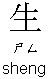 :
: 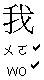
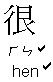
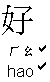 ,
, 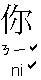
 ?
? 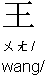
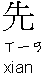
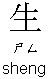 :
: 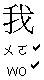
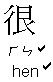
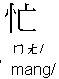 .
. 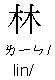
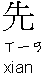
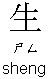 :
: 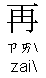
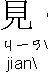 ,
, 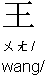
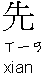
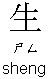 .
. 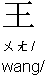
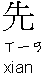
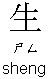 :
: 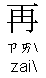
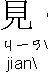 .
.
Mr. Wang : Good morning Mr. Lin. How are you?
Mr. Lin : I am fine, and you?
Mr. Wang : I am very busy.
Mr. Lin: Goodbye, Mr. Wang.
Mr. Wang: Goodbye.
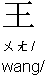
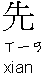
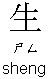 : Mr. Wang
: Mr. Wang 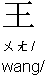 : 1) a sure name; 2) king
: 1) a sure name; 2) king
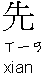
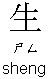 : "mister"
: "mister"

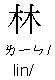 : 1) a sure name; 2) forest
: 1) a sure name; 2) forest

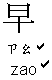 : 1) early; 2) good morning
: 1) early; 2) good morning

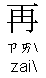
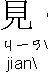 : Goodbye; see you (again); so long
: Goodbye; see you (again); so long 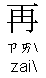 : again
: again

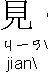 : see
: see

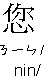
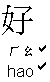
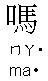 : How are you ?
: How are you ? 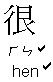 : very
: very

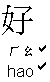 : good, fine, well
: good, fine, well

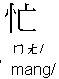 : busy
: busy

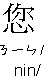 : you (polite form)
: you (polite form)

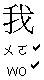 : first person singular: "I", "me" (Chinese does not distinguish
between subject and object pronouns)
: first person singular: "I", "me" (Chinese does not distinguish
between subject and object pronouns)

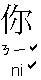 : you (informal form and person singular)
: you (informal form and person singular)

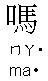 :
indicate question (always tagged at the end of the sentence)
:
indicate question (always tagged at the end of the sentence)

 :
sentence partical "and how about..." always tagged at the end
of the sentence
:
sentence partical "and how about..." always tagged at the end
of the sentence


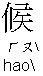 : Greeting
: Greeting | S | (A) | SV |
|---|---|---|
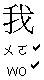 |
(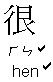 ) ) |
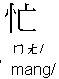 . .
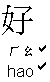 . .
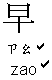 . . |
(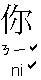 ) )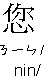 |
||
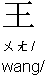 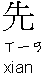 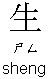 |
||
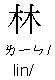 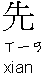 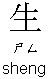 |
Note for Stative Verbs (SV):
In Chinese, we just say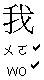
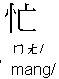 (I busy), without the verb to be.
(I busy), without the verb to be.
Thus, 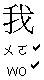
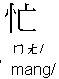 = I am busy
= I am busy
Stative Verbs such as 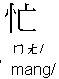 ,
,
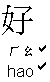 or
or 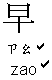 are used in the same way.
are used in the same way.
| S | SV | QW |
|---|---|---|
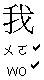 |
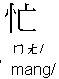
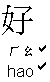 |
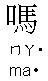 ? ? |
(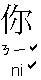 ) )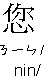 |
||
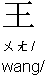 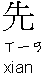 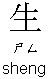 |
||
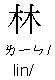 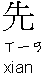  |
Note for Question Word (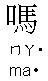 ) :
) :
We add 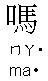 in
the end of a Chinese statement to make a question sentence without changing
the words order.
in
the end of a Chinese statement to make a question sentence without changing
the words order.
| S | (A) | SV | T.-Q
|
|---|---|---|---|
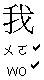 |
(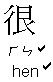 ) ) |
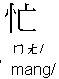 . .
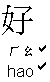 . .
|
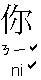  ? ? |
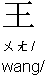 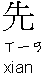 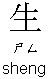 |
|||
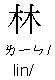 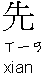 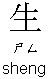 |
Note:
"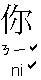
 ?
" or "
?
" or " 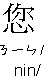
 ?
" is a "Tag-question"; usually we add it in the end of a
sentence to form a short "counter-question".
?
" is a "Tag-question"; usually we add it in the end of a
sentence to form a short "counter-question".
4. Greeting : "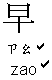 "
"
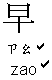 .
.
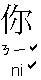
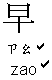 .
.
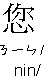
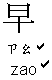 .
.
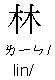
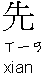
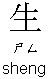 ,
,
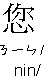
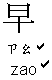 .
.
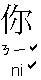
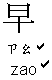 "
or "
"
or " 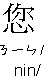
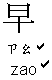 "
as "Good morning" in English.
"
as "Good morning" in English.
We can also say "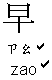 "
only.
"
only.